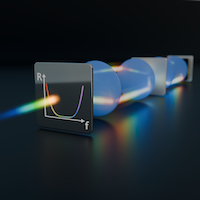
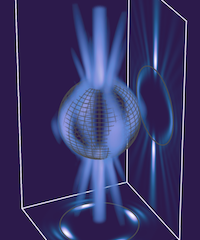
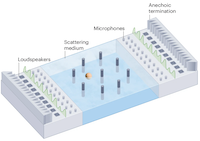
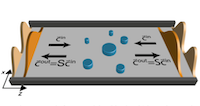
In collaboration with Ori Katz’s team, we have shown in this Letter how to design an optical cavity such that a weakly absorbing film inside of it can perfectly absorb coherent laser light that is both spatially and spectrally broadband. Congratulations to Helmut and Lena for developing the theory behind this concept and many thanks to Oliver for the nice figure here on top!